
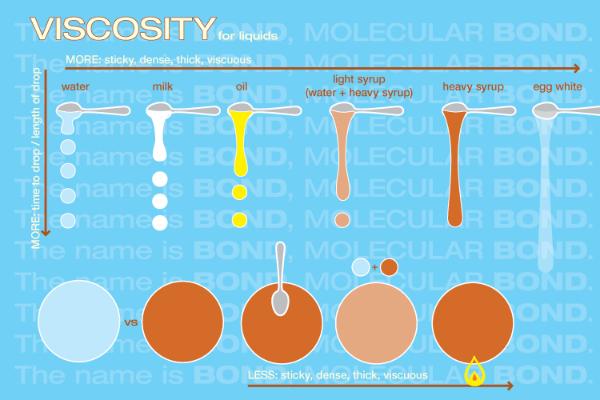
Density in liquids is defined as the amount of mass that may be filled in a cubic meter of volume. Oil floats on water because its density is lower than that of water. The unit of viscosity is newton-second per square meter, which is usually expressed as pascal-second in SI units. In contrast, turbulent flow is a type of fluid in which the fluid fluctuates and mixes irregularly. Laminar flow is a form of fluid (gas or liquid) flow in which the fluid flows smoothly and in predictable patterns. Fluids that have no or minimal internal friction resistance are categorized as non-viscous fluids. The degree of resistance between the fluid layers is measured by viscosity, which is a fluid factor. The viscous fluid is defined as a fluid with a high flow resistance. Its alternative units are newton-second per square meter (N s m-2) and pascal-second (Pa s.) The SI unit of viscosity is poiseiulle (PI). Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. Newtons Law of ViscosityĪccording to Newton’s viscosity law, “shear stress is directly proportional to velocity gradient.” The negative value of the velocity gradient between two adjacent fluid layers is directly proportional to the shear stress between the two adjacent fluid layers. The viscosity of water changes with its temperature, and the greater the temperature, the less viscous the water becomes. Viscosity of WaterĪt 20 ☌, water has a viscosity of 1.0016 millipascals second. It is calculated by measuring the time in seconds necessary for a set volume of fluid to flow a known distance through a capillary within a calibrated viscometer at a carefully regulated temperature. The internal resistance to the flow of a fluid under gravitational forces is measured by kinematic viscosity. Some Examples of viscosity Or viscous substances are:
The unit of dynamic viscosity μ is centipoise. Dynamic viscosity is related to kinematic viscosity by the equation μ = ρv where ρ is the density of the fluid. Gas viscosity is often lower than liquid viscosity.

The viscosity coefficient is a measurement of the fluid’s resistance to flow. The relationship between viscous and inertial forces in a fluid is known as kinematic viscosity. The relationship between shear stress and shear rate in a fluid is known as dynamic viscosity. Kinematic and dynamic viscosity are the two types of viscosity that are usually reported. A fluid with low viscosity flows easily because its molecular structure causes very little friction when it is in motion. A fluid with a high viscosity resists motion because its molecular structure causes a lot of internal friction. Viscosity describes the internal friction of a moving fluid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
